Memory Card: Difference between revisions
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
Service 2 is used to set key, that is obtained from memory card, into slot 0x1C of SceSblDMAC5DmacKRBase keyring. | Service 2 is used to set key, that is obtained from memory card, into slot 0x1C of SceSblDMAC5DmacKRBase keyring. | ||
For encryption during memory card auth Msif driver uses 3-DES-CBC-CTS cipher. | |||
{| | {| | ||
Revision as of 23:27, 2 July 2018
Partitions
Memory Card can be accessed with SceMsif module. It has the following partitions:
| code | type | name | desc |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0xD | raw | Some data | |
| 0x8 | exfat | ux0 | Memory Card |
Findings about Memory Card
It turns out that memory card supports standard Memory Stick protocol (TPC).
Msif driver allows to read and write single values on memory card according to the (TPC) protocol.
It can also read and write chunks of data from memory card using (TPC) protocol.
It is still not confirmed, however based on some findings in Msif driver, it is hypothesized that Vita`s memory card is simply new generation of memory stick with additional auth layer.
If auth layer can be faked, it could probably be possible to use usual memory stick with Vita.
Memory Card Initialization
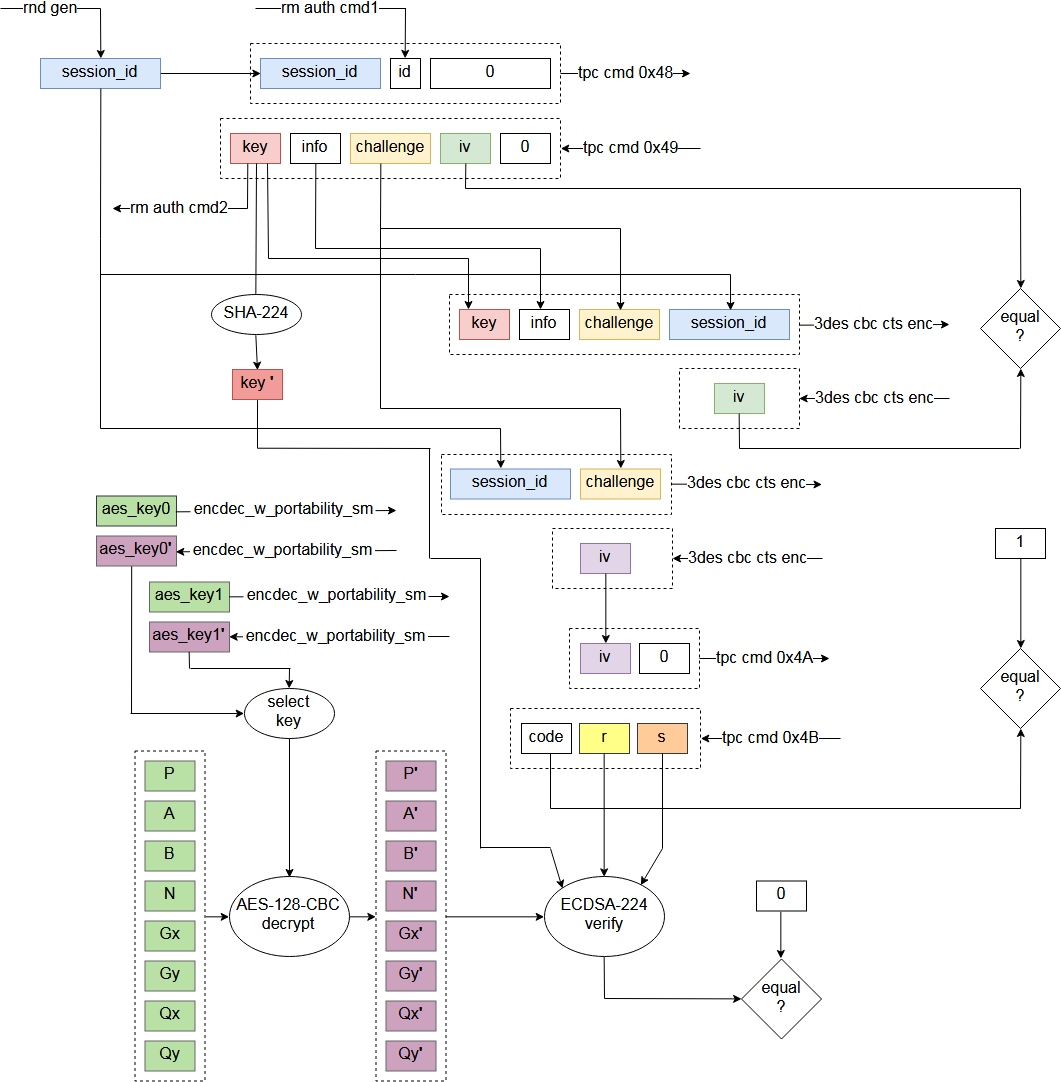
Much like SD standard allows execution of vendor specific commands through CMD56, Vita`s memory card has specific commands 0x48, 0x49, 0x4A and 0x4B.
To be able to read from memory card, it has to be properly initialized with commands 0x48 and 0x49 first.
It is not completely tested yet, but commands 0x4A and 0x4B are probably not required, and used by Vita to check that memory card is genuine.
Memory card initialization also uses F00D rm auth services 1 and 2.
Service 1 is used to obtain some data from F00D (1 byte).
Service 2 is used to set key, that is obtained from memory card, into slot 0x1C of SceSblDMAC5DmacKRBase keyring.
For encryption during memory card auth Msif driver uses 3-DES-CBC-CTS cipher.